Table of Contents
Most people think of large-scale injection moulding and picture huge factories producing numerous identical plastic pieces. However, what if you only need a few hundred or a few thousand pieces? Start-ups, product developers, and niche industries need speed and flexibility rather than sheer volume. This is where Low Volume Injection Molding comes in, debunking the myth that this manufacturing process is only for mass production.
In this post, I will answer how the process works, what the main advantages are, when to use it, and how to choose the right materials for a given project.
How Low-Volume Plastic Injection Works
At its core, the process of low volume plastic injection moulding is quite similar to traditional injection moulding. The most important difference, however, can be seen in the tooling.
With traditional mass manufacturing, the mould is made of hardened steel, which is very strong but also expensive and takes a long time to make. On the other hand, the mould for plastic injection moulding services of smaller volume is most likely to be made of softer materials like aluminium.
The low-volume aluminium moulds can be manufactured with greater rapidity and at a lower cost. Aluminium can dissipate heat at a faster rate than steel, leading to quicker heating and cooling cycles during the moulding process. As a result, lower volume production cycles can be accomplished at a faster rate, leading to a greater market efficiency achieved by companies.
The Benefits of Low-Volume Injection Moulding
The low-volume manufacturing option has specific advantages for companies that require flexibility and the ability to control costs.
Cost Efficiency
The greatest benefit is that the upfront tooling costs are reduced significantly. For many small start-up companies and for new projects where the market demand is uncertain, the costs of building a hardened steel mould that is clearly in the thousands of pounds may simply not be affordable. On the other hand, the costs of aluminium moulds that allow high quality moulding are available for a small fraction of that cost. This means that the companies will not have to spend a massive amount as capital to pour into the business and allows for better allocation of other resources, for example, spending on advertising or product development.
Faster Time to Market
In many industries, there’s a big advantage to being the first to market, and in those situations, speed is critical. The low-volume method is significantly faster in the mould making and first plastic part production process. For example, the aluminium mould is produced in a few weeks as opposed to the many months that are required for steel moulds. This speed of production will allow the company to market the product quickly, obtain feedback and refine the product in iterations faster than their competition.
Design Flexibility
There is hardly any clear direction to product development as there is testing, feedback, and revisions. Low-volume moulding fits best into this scenario. Moulding aluminium is easier to adjust and is cheaper, as well as being easier to construct. In the event of a design flaw or revision that needs to be upgraded, it costs much less to modify than to change some of the design into an expensive hardened steel. This modification gives designers and engineers the power to refine their product, and not be bound by the costs that come with the production of mass tooling.The process of product development is usually not linear as it mostly involves a number of iterations, feedback, tests and refinements.
When to Use Low-Volume Injection Moulding
This technique is not just a temporary option; it is a purposeful approach to a number of situations. Knowing when to implement this technique offers a useful competitive advantage.
Bridge Production
Picture this scenario: your product is ready to be launched, but the permanent steel moulds are still weeks or months away from being completed, meaning your product is likely to miss a critical market window. Low-volume injection moulding serves as a perfect ‘bridge’ because you are able to produce an initial batch of several thousand units to meet early demand. This step allows your product launch to stay on schedule while the high-volume tooling is being completed.
Market Testing
There is always a level of uncertainty when launching a new product. Will customers like the design? Is the correct set of features present? Instead of making the less desirable decision of producing hundreds of thousands of units based on assumptions, you can use low-volume moulding to do a pilot run. If you produce between 500 to 5,000 units, you are able to test the market, get feedback and validate demand. This approach reduces the likely financial risks while ensuring your product is something that real customers want.
Niche Markets and Customisation
Not every product is suited to a global marketplace. There are many industries, including aerospace, medical device fabrication, and custom industrial machinery, that need outsized and top-quality components, but in limited quantities. In these niche markets, low-volume production can be a perfect fit. It enables plastic part manufacturers to make highly specialised parts such as custom surgical instruments and tailored automotive components, without the overhead burden associated with the economics of mass production. It is also a niche of perfection for the production of limited edition products, or to provide bespoke customisation of existing products.
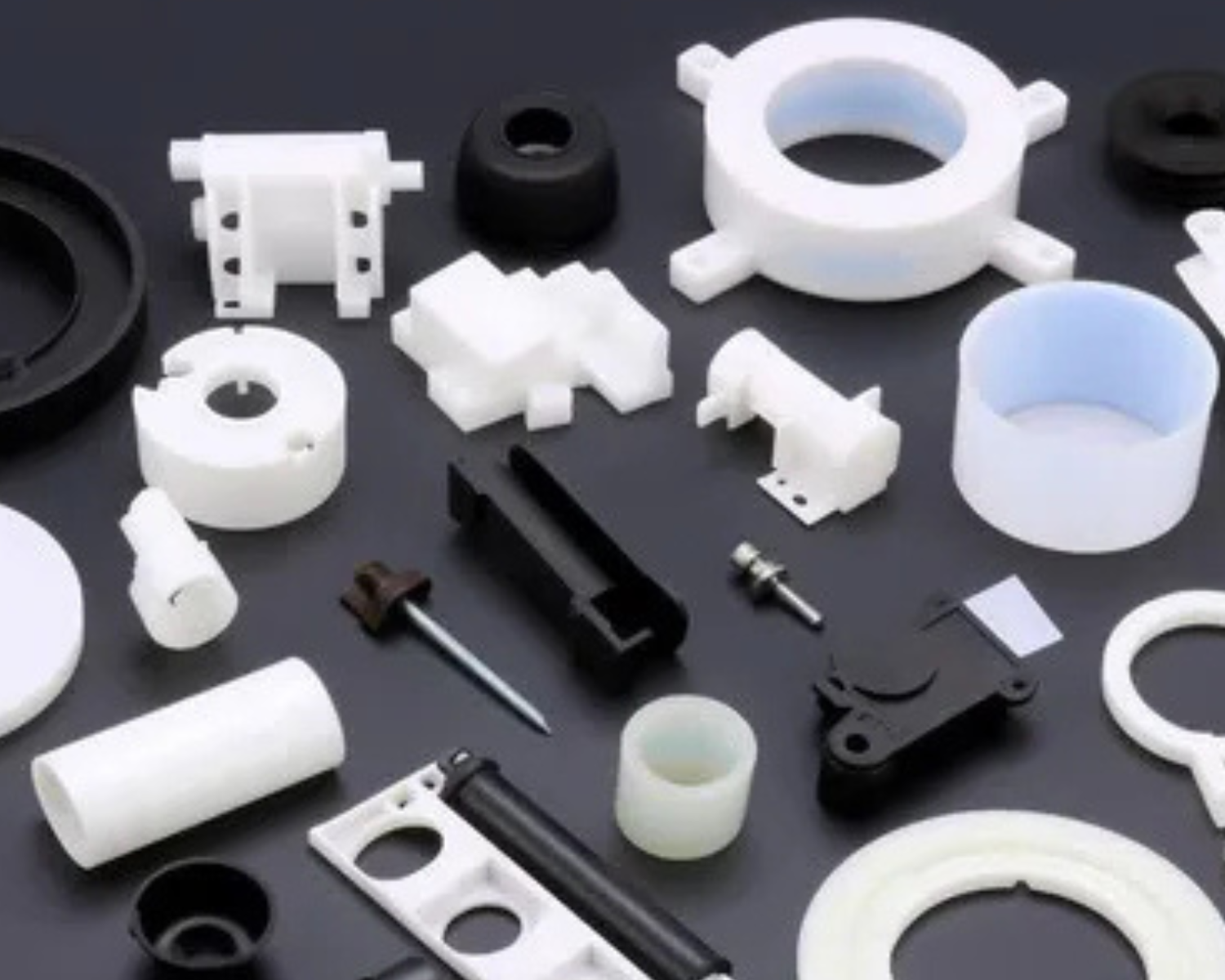
Determining Which of the Injection Molded Plastics to Use
There is a common misconception that the range of materials to use is restricted with a low volume of production. That is not the case. With low volume plastic injection moulding there is access to the same production-grade thermoplastics that are available in high volume manufacturing, allowing your parts to achieve the functional and aesthetic features desired.
When choosing these materials some of the factors to consider are:
- Strength and Damage Tolerance: If an exposed part is likely to face significant stress and damage, the recommended materials are Polycarbonate (PC) or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS).
- Flexibility: If there is a requirement for the part to bend or flex without breaking such as in living hinges or snap-fit components, Polypropylene (PP) is a flexible and inexpensive choice.
- Temperature: In cases where exposure to high temperatures can be encountered, PEEK or Ultem (PEI) materials are a recommended choice due to their great thermal stability.
- Aesthetics and Finish: If the part is required to look visually appealing, ABS or Acrylic (PMMA) materials should be used because of their great surface finish and ease of colouring or texturing.
- Chemical: Exposure of the part that is enclosed to chemicals, oils or solvents should be able to be resisted and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) or Nylon (PA) are a good choice.
Getting to know your custom plastic fabrication partner is imperative. Their expertise in material science will help find the right thermoplastic for your application while being mindful of your budget.
Applications of Low-volume injection molding
Low-volume injection molding is already driving innovation across various industries:
– Medical: Developing housings for bespoke diagnostic instruments, surgical instrument handles, and orthopedic models tailored to patients.
– Automotive: Producing custom aftermarket parts, limited edition vehicles’ interior trim, and functional dashboard prototype components.
– Consumer Electronics: Offering limited edition gadget casings, custom IoT device enclosures, and parts for wearable tech.
– Aerospace: Fabricating drone interior components, custom lightweight parts, and high-performance brackets in low quantities.
Discover Your Optimal Manufacturing Strategy
For businesses of any size, we offer a rapid, affordable, and high-quality option in low volume plastic injection moulding. No more waiting in long queues at large manufacturing facilities to access high-quality, expert-grade plastic components; low volume plastic injection moulding is the perfect option to launch new products, cater to specialised markets, and expedite the manufacturing process.
If you’re prepared to progress out of the prototype stage, this cost-effective and low-risk method could work best for your next project.
Want to learn how low volume injection moulding helps get your products into the market sooner? Get in touch with us and we can set up a consultation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is low volume injection moulding quality the same as mass production?
A: Absolutely! The only thing different is not the quality of the component, but the type of mould used (it’s aluminium as opposed to steel). The injected components come from the same production-grade thermoplastics as the high-volume parts.
Q:What is considered low volume?
A:Low volume is the middle ground between single prototypes and mass production of millions of items. The term low volume is usually used to describe production runs between 100 – 100,000 units.
Q:How much money does using aluminium moulds save?
A:Aluminium tooling is easier and faster to machine, so, while every project is different, costs can fall in the range of 40% – 60% of the price of more traditional hardened steel tooling.
Q:Can I change my design after the mould is made?
A:In low volume moulding, it can be easier and more economical to adjust designs from an aluminium mould than from one made of hardened steel. However, if design changes are being made, it’s important to approach the changes with caution. It’s true that more steel can be added, but removing metal is much of the challenge.
Q: How fast can I get my parts?
A: It sometimes depends on what the part is but with low volume tooling, we can get parts made in 2 to 4 weeks instead of the normal 8 to 12 weeks it usually takes with steel production moulds.






